Stockholders’ equity is decreased by all of the following except, a crucial concept in corporate finance, presents a comprehensive overview of the factors that contribute to the reduction of stockholders’ equity, providing valuable insights into the financial health and stability of organizations.
This discussion delves into the impact of dividends, share repurchases, asset impairments, treasury stock transactions, and stock-based compensation on stockholders’ equity, exploring their accounting treatments and implications for financial statements.
Impact of Dividends on Stockholders’ Equity
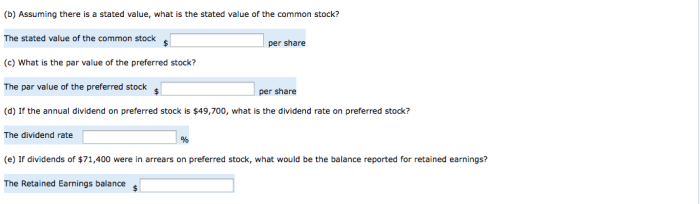
The payment of dividends reduces stockholders’ equity because it represents a distribution of the company’s earnings to its shareholders. When a company declares a dividend, the amount of the dividend is deducted from the retained earnings account, which is a component of stockholders’ equity.
The reduction in retained earnings results in a decrease in stockholders’ equity.
Accounting Treatment of Dividends
- The declaration of a dividend creates a dividend payable liability.
- The payment of the dividend reduces the dividend payable liability and retained earnings.
- The impact on the balance sheet is a decrease in both assets (cash) and stockholders’ equity (retained earnings).
Examples of How Dividends Affect the Balance Sheet
- If a company declares a $1 million dividend and has $5 million in retained earnings, its retained earnings will decrease to $4 million after the dividend is paid.
- If the company has $2 million in cash, the payment of the dividend will reduce its cash balance to $1 million.
Repurchase of Shares and Stockholders’ Equity
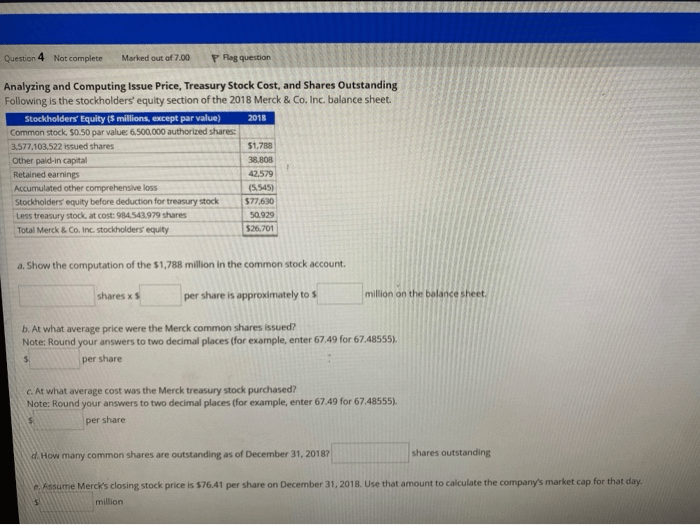
The repurchase of shares reduces stockholders’ equity because it represents a reduction in the number of shares outstanding. When a company repurchases its own shares, the shares are retired, which reduces the total number of shares in circulation. The reduction in shares outstanding results in an increase in the book value per share, but a decrease in total stockholders’ equity.
Impact of Share Repurchases on Stockholders’ Equity
- Treasury Stock Method: The repurchased shares are recorded as treasury stock and are not included in the calculation of stockholders’ equity.
- Retained Earnings Method: The repurchased shares are recorded as a reduction in retained earnings, which is a component of stockholders’ equity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Share Repurchases
Advantages
- Increase book value per share
- Reduce dilution from stock options and convertible debt
- Signal confidence in the company’s future prospects
Disadvantages
- Reduce total stockholders’ equity
- Can be expensive if the stock price is high
- May not always be tax-efficient
Impairment of Assets and Stockholders’ Equity
The impairment of assets reduces stockholders’ equity because it represents a reduction in the carrying value of an asset. When an asset is impaired, the difference between the carrying value and the fair value is recognized as an expense. The expense is recorded on the income statement and reduces retained earnings, which is a component of stockholders’ equity.
Accounting Treatment of Asset Impairments
- The impairment loss is recognized on the income statement as an operating expense.
- The carrying value of the asset is reduced to its fair value.
- The impact on the balance sheet is a decrease in both assets and stockholders’ equity (retained earnings).
Examples of Asset Impairments that Impact Equity
- If a company’s inventory becomes obsolete, the company may have to write down the value of the inventory. The write-down would result in an impairment loss and a reduction in stockholders’ equity.
- If a company’s property and equipment becomes impaired, the company may have to write down the value of the assets. The write-down would result in an impairment loss and a reduction in stockholders’ equity.
Treasury Stock and Stockholders’ Equity
Treasury stock is a company’s own shares that have been repurchased but not retired. Treasury stock is not considered outstanding and does not have any voting rights. The purchase and sale of treasury stock can impact stockholders’ equity.
Impact of Treasury Stock on Stockholders’ Equity, Stockholders’ equity is decreased by all of the following except
- Purchase of Treasury Stock: The purchase of treasury stock reduces cash and stockholders’ equity (retained earnings) by the cost of the shares.
- Sale of Treasury Stock: The sale of treasury stock increases cash and stockholders’ equity (retained earnings) by the proceeds from the sale.
Accounting Treatment of Treasury Stock Transactions
- The purchase of treasury stock is recorded as a reduction in cash and a reduction in stockholders’ equity (retained earnings).
- The sale of treasury stock is recorded as an increase in cash and an increase in stockholders’ equity (retained earnings).
Stock-Based Compensation and Stockholders’ Equity: Stockholders’ Equity Is Decreased By All Of The Following Except
Stock-based compensation is a form of compensation that is granted to employees in the form of shares of the company’s stock. Stock-based compensation reduces stockholders’ equity because it represents an increase in the number of shares outstanding. The increase in shares outstanding results in a decrease in the book value per share and total stockholders’ equity.
Accounting Treatment of Stock-Based Compensation
- The expense associated with stock-based compensation is recognized on the income statement over the vesting period of the award.
- The number of shares issued is recorded as an increase in the number of shares outstanding.
- The impact on the balance sheet is a decrease in stockholders’ equity (retained earnings) and an increase in total liabilities (if the award is a liability).
Examples of How Stock-Based Compensation Affects the Income Statement and Balance Sheet
- If a company grants stock options to its employees, the expense associated with the options will be recognized on the income statement over the vesting period of the options. The number of shares that could be issued upon exercise of the options will be recorded as an increase in the number of shares outstanding.
- If a company grants restricted stock units to its employees, the expense associated with the units will be recognized on the income statement over the vesting period of the units. The number of shares that will be issued upon vesting of the units will be recorded as an increase in the number of shares outstanding.
FAQ
What are the primary factors that reduce stockholders’ equity?
Stockholders’ equity is primarily decreased by dividend payments, share repurchases, asset impairments, and stock-based compensation.
How does the payment of dividends impact stockholders’ equity?
Dividend payments directly reduce stockholders’ equity, as the company distributes a portion of its retained earnings to shareholders.
What is the accounting treatment for asset impairments?
Asset impairments involve recognizing a loss on the balance sheet, which reduces both the asset’s carrying value and stockholders’ equity.