Embark on a scientific odyssey with Intermolecular Forces and Strengths POGIL, a comprehensive exploration into the intricate world of molecular interactions. This engaging journey unveils the fundamental forces that govern the behavior of substances, shaping their properties and dictating their reactivity.
As we delve into this molecular realm, we will decipher the diverse types of intermolecular forces, unravel their relative strengths, and witness their profound influence on the physical and chemical properties of matter. Prepare to be captivated as we unravel the secrets of intermolecular interactions, empowering you with a deeper understanding of the molecular tapestry that weaves our world.
Intermolecular Forces
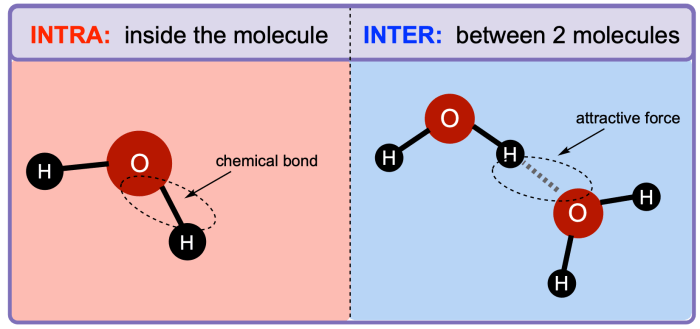
Intermolecular forces (IMFs) are the attractive forces between molecules. They are weaker than the intramolecular forces that hold atoms together within a molecule. IMFs are responsible for many of the physical properties of substances, such as melting point, boiling point, and solubility.
There are three main types of IMFs:
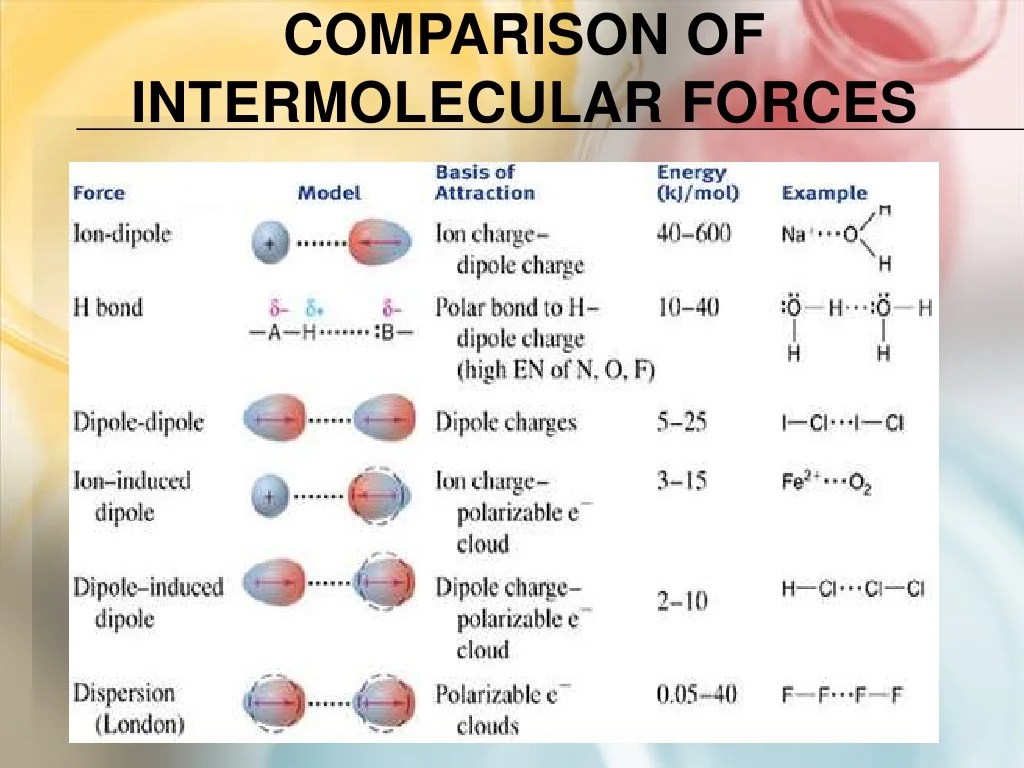
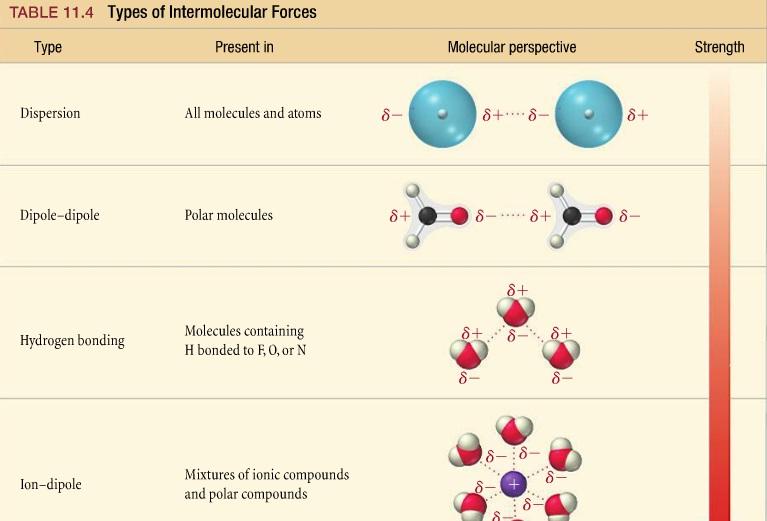
- Dipole-dipole forcesoccur between polar molecules, which have a permanent dipole moment. The positive end of one molecule is attracted to the negative end of another molecule.
- Hydrogen bondingis a special type of dipole-dipole force that occurs between molecules that have a hydrogen atom bonded to a small, highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. Hydrogen bonding is stronger than dipole-dipole forces.
- London dispersion forcesare weak, temporary forces that occur between all molecules, even nonpolar molecules. London dispersion forces are caused by the instantaneous, random fluctuations in the electron distribution of molecules.
Properties of Substances, Intermolecular forces and strengths pogil
IMFs affect the physical properties of substances in several ways.
- Melting point: Substances with strong IMFs have higher melting points because more energy is required to overcome the attractive forces between the molecules.
- Boiling point: Substances with strong IMFs have higher boiling points because more energy is required to overcome the attractive forces between the molecules and vaporize the liquid.
- Solubility: Substances with strong IMFs are less soluble in nonpolar solvents because the IMFs between the solute and solvent molecules are weaker than the IMFs between the solute molecules themselves.
Phase Changes
IMFs also affect phase changes. A phase change is a change in the physical state of a substance, such as from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas. Phase changes involve changes in the IMFs between the molecules.
When a substance melts, the IMFs between the molecules are overcome and the molecules become more mobile. When a substance boils, the IMFs between the molecules are completely overcome and the molecules become a gas.
| Phase Change | Intermolecular Forces Involved |
|---|---|
| Solid to liquid (melting) | Overcoming of IMFs |
| Liquid to gas (boiling) | Complete overcoming of IMFs |
| Gas to liquid (condensation) | Formation of IMFs |
| Liquid to solid (freezing) | Strengthening of IMFs |
Chemical Reactions
IMFs can also affect the rates of chemical reactions. Reactions between substances with strong IMFs tend to be slower because the IMFs must be overcome before the reactants can come together and react.
IMFs can be used to control the rates of reactions. For example, adding a solvent that has strong IMFs can slow down a reaction by solvating the reactants and preventing them from coming together.
Question Bank: Intermolecular Forces And Strengths Pogil
What are the different types of intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces encompass a range of interactions, including dipole-dipole forces, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces (London dispersion forces and permanent dipole-induced dipole forces).
How do intermolecular forces affect the properties of substances?
Intermolecular forces govern various physical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, and solubility. Substances with stronger intermolecular forces tend to have higher melting and boiling points, as well as lower solubility in nonpolar solvents.
What role do intermolecular forces play in phase changes?
Intermolecular forces determine the energy required for phase changes. Substances with strong intermolecular forces require more energy to overcome these forces, resulting in higher melting and boiling points.
How do intermolecular forces influence reaction rates?
Intermolecular forces can hinder the movement of reactants, affecting reaction rates. Substances with strong intermolecular forces tend to react more slowly due to the increased energy barrier that must be overcome.