GFCI stands for which of the following: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. GFCIs are an essential component of electrical safety, designed to protect against electrical shocks and prevent electrical fires. This comprehensive guide will delve into the definition, types, installation, testing, maintenance, applications, troubleshooting, and safety considerations of GFCIs, providing a thorough understanding of their crucial role in electrical systems.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Definition of GFCI
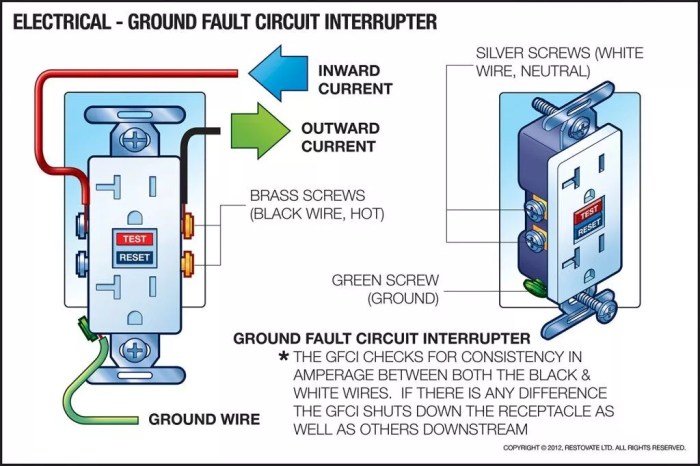
GFCI stands for Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. It is a safety device designed to protect individuals from electrical shock by interrupting the flow of electricity when a ground fault occurs.
A ground fault is an unintended path for electrical current to flow to the ground instead of completing the circuit back to the electrical panel. This can occur when an electrical appliance or wiring becomes damaged, allowing current to leak to the ground through the user or other conductive materials.
Types of GFCIs

There are two main types of GFCIs:
- Circuit Breaker GFCIs: These are installed in a circuit breaker panel and protect all outlets and fixtures on the circuit.
- Receptacle GFCIs: These are installed in individual outlets and protect only that outlet.
Circuit breaker GFCIs are generally more expensive than receptacle GFCIs, but they offer more comprehensive protection. Receptacle GFCIs are less expensive and easier to install, but they only protect the individual outlet where they are installed.
Installation and Wiring of GFCIs
GFCIs must be installed by a qualified electrician in accordance with local electrical codes.
Circuit breaker GFCIs are installed in the circuit breaker panel by connecting them to the bus bars and the circuit wires.
Receptacle GFCIs are installed in individual outlets by connecting them to the outlet box and the incoming and outgoing wires.
Testing and Maintenance of GFCIs
GFCIs should be tested regularly to ensure they are functioning properly.
To test a GFCI, simply press the “Test” button. The GFCI should trip, interrupting the flow of electricity. If the GFCI does not trip, it should be replaced.
GFCIs should also be inspected regularly for any signs of damage or wear.
Applications of GFCIs
GFCIs are required by code in all areas where there is a risk of electrical shock, such as:
- Bathrooms
- Kitchens
- Laundry rooms
- Outdoor areas
GFCIs can also be used in other areas where there is a risk of electrical shock, such as:
- Workshops
- Garages
- Construction sites
Troubleshooting GFCIs: Gfci Stands For Which Of The Following
If a GFCI is not working properly, there are a few things you can do to troubleshoot the problem:
- Make sure the GFCI is turned on.
- Press the “Reset” button on the GFCI.
- Check the circuit breaker or fuse for the GFCI circuit.
- Check the wiring connections to the GFCI.
If you are unable to troubleshoot the problem yourself, you should contact a qualified electrician.
Safety Considerations
GFCIs are an important safety device that can help to prevent electrical shock.
It is important to remember that GFCIs are not foolproof. They can only protect against electrical shock if they are installed and maintained properly.
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing and maintaining GFCIs.
Top FAQs
What is the primary function of a GFCI?
GFCIs are designed to detect imbalances in electrical current, which can occur when electricity escapes from its intended path and flows through an unintended path, such as through a person’s body. When a GFCI detects such an imbalance, it quickly interrupts the electrical circuit, preventing the flow of electricity and reducing the risk of electrical shock.
Where are GFCIs typically required to be installed?
GFCIs are required by electrical codes to be installed in specific areas where there is a higher risk of electrical shock, such as bathrooms, kitchens, garages, and outdoor areas. These areas are more likely to have moisture or water present, which can increase the risk of electrical hazards.
How often should GFCIs be tested?
GFCIs should be tested regularly, typically once a month, to ensure they are functioning properly. Testing involves pressing the “Test” button on the GFCI, which simulates a ground fault and trips the circuit if the GFCI is working correctly.